The National Cancer Institute says that weight gain is a major risk factor for developing breast cancer. Gaining weight in adulthood appears to increase the risk of breast cancer before and after menopause. One large study found that women who gained about 20 pounds after age 18 had a 15% higher risk of breast cancer compared to women who gained little or no weight. Women who gained 55 pounds or more had a 45% higher risk. It is important for both men and women to keep a healthy weight. Managing weight is a challenge for most people in the U.S. In Fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 69% of American adults are over weight.
Obesity & The Risk Of Heart Disease
The perfect gift this Valentine’s Day is the gift of heart health. Along with Valentine’s Day, February marks American Heart Month, a great time to commit to a healthy lifestyle and make small changes that can lead to a lifetime of heart health. Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States. Every year, 1 in 4 deaths are caused by heart disease. The good news? Heart disease can often be prevented when people make healthy choices and manage their health conditions. Communities, health professionals, and families can work together to create opportunities for people to make healthier choices. The American Heart Association recommends obese patients participate in a medically supervised weight loss program to reduce the risk of heart disease.
HOW MANY RISK FACTORS DO YOU HAVE?
Major Risk Factors: are those that research has shown significantly increase the risk of heart disease. The more risk factors you have, the greater your chance of developing it.
High Blood Cholesterol
High Blood Pressure
Physical Inactivity
Obesity / Overweight
Smoking
Diabetes
Poor Diet
(Modifiable: Any person can make changes to these risk factors listed above, even modest improvement to your health will make a big difference.)
Age
Gender
Family History
(Non-Modifiable: These risk factors cannot be changed.)
7 SEVEN KEYS TO PREVENTION
Reduce Blood Sugar
Control Cholesterol
Manage Blood Pressure
Stop Smoking
Eat Right
Lose Weight
Get Moving
ARE YOU MAKING AN EFFORT OR MAKING EXCUSES?
12% say they are too busy taking care of others to take care of themselves.
27% live a heart-healthy lifestyle.
17% say they don’t have time to exercise regularly.
18% doesn’t want to stop eating foods they like.
14% say it costs too much to eat healthy.
7% doesn’t know how to take care of their heart.
14% doesn’t like exercising.
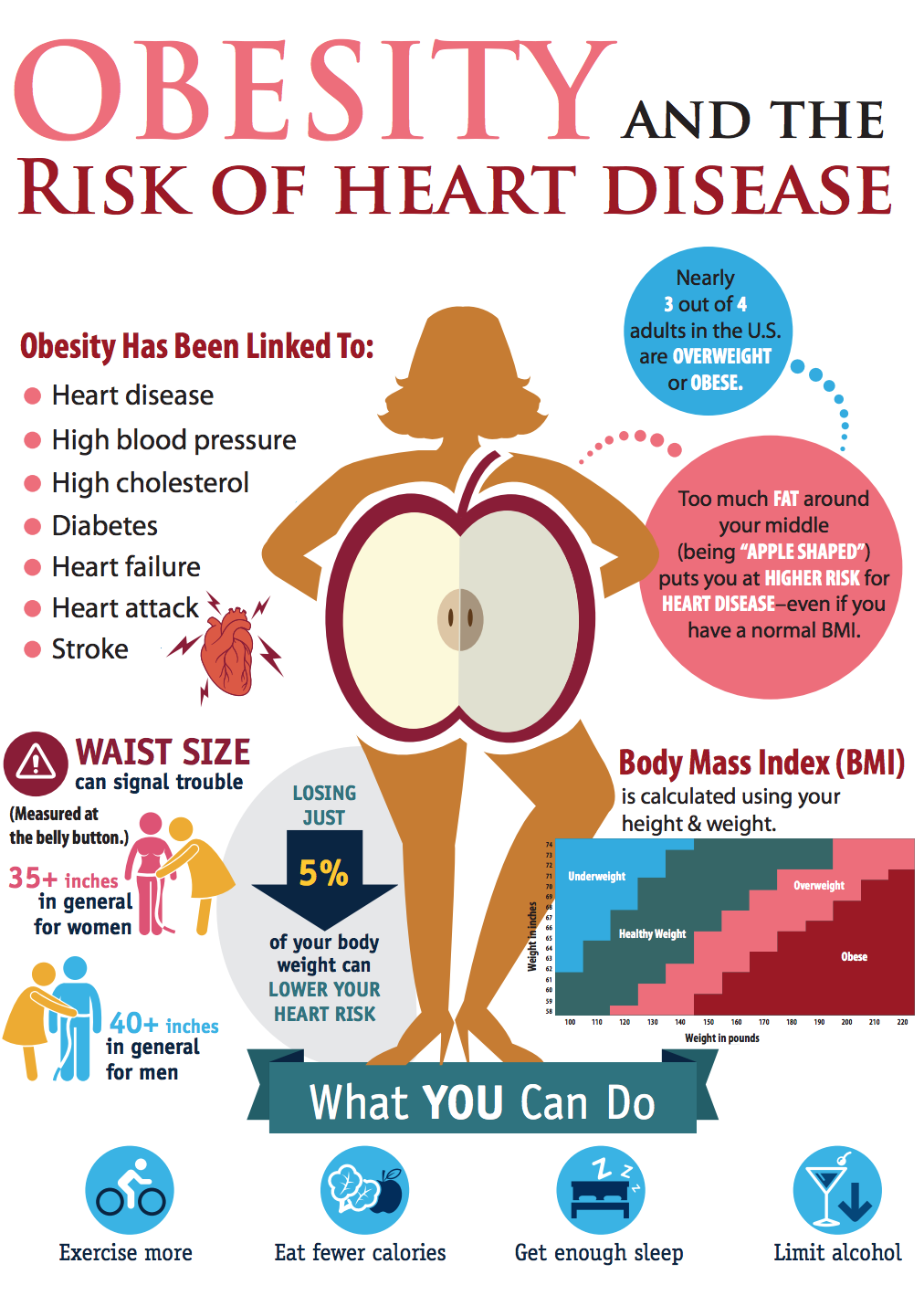
Obesity
Obesity is the leading cause of diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol and heart disease. 33% of U.S. adults are obese and 1 in 4 deaths are caused by heart disease.
Know your waist circumference:
Waist circumference is far more accurate than the Body Mass Index (BMI). Make sure to measure at your belly button.
Males: Greater than 40 inches equals obesity and increased risk for heart disease.
Females: Greater than 35 inches equals obesity and increased risk for heart disease.
Alcohol And It’s Impact On The Body
Alcohol use—as a well-established part of human culture—is something that has become almost as acceptable as eating and breathing. As a social facilitator and feel good drug of choice for many, alcohol is very popular indeed, with consumption at mass levels. One effect of alcohol, which is not widely discussed, is its impact on body composition. In its purest form, ethyl alcohol, which supplies seven calories per gram, provides energy, bumping up ones total energy balance whenever it is consumed. Unlike macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins and fats, alcohol supplies what we often refer to as empty calories: calories without nutrition. To make matters worse, it is the first fuel to be used when combined with carbohydrates, fats and proteins, postponing the fat-burning process and contributing to greater fat storage.
4 Ways Alcohol Hinders Weight Loss
1. Alcohol Supplies Almost Twice As Many Calories As Protein And Carbs At seven calories per gram, alcohol supplies almost twice as many as protein and carbohydrates. In fact, alcohol has only two fewer calories than fat, which has nine per gram. It must also be remembered that the calories in alcohol lack the nutrients beneficial for a healthy metabolism and will therefore hasten fat storage. The calories found in the average alcoholic drink are quite concentrated compared to many foods, and this actually causes one to inadvertently take in many more calories than would otherwise be consumed. Alcohol is quite deceptive in that it passes through the system rapidly, often before the drinker is aware of the number of drinks they have had.
2. Alcohol Loosens The Inhibitions While drinking, people usually will not stop to consider the impact alcohol is having on their bodies; such is alcohol's affect on loosening the inhibitions. The result of this relaxed thinking could mean more calories consumed and extra body fat gains. Those drinking might also eat more of the wrong kinds of food, without thinking of the consequences. Alcohol tends to have an appetite stimulating effect as it provides little in the way of nutrition, leaving a craving for other foods at the time of consumption. Add this to the fact that fatty and salty foods tend to accompany most occasions featuring alcohol (as well as alcohol actually stimulating one's appetite for these kinds of foods), and the general loosening of resolve that goes with an inebriated mindset, and you have a recipe for excess fat gain. Alcohol has also been shown to affect motivation, making a healthy diet harder to stay on while it is being used.
3. Alcohol Can Damage The Stomach, Kidneys, And Liver Given alcohol is a by-product of yeast digestion; it can have an irritating effect on the lining of the stomach and gradually weaken the kidneys and liver, leading to serious health problems—even death in certain instances. Any weakening of the stomach will lessen the rate and efficiency at which food is digested, which ultimately interferes with a healthy metabolism and the weight loss process. The liver—which processes toxins and breaks down fats for fuel—is crucial when it comes to maintaining a healthy body composition. Alcohol is at its most destructive during the liver's detoxification process.
4. Alcohol Increases Appetite Touched on briefly in point two, alcohol can increase appetite, making the combination of alcohol and a fattening meal all the more worse. A study showed that alcohol consumed before a meal increased caloric intake to a far greater extent than did a carbohydrate drink.
Blood Pressure Education Month
High Blood Pressure, also know as Hypertension, increases the risk of serious diseases and conditions such as heart disease and stroke. In the US, heart disease is the most common form of death and stroke is the third leading cause. Other risk factors of high blood pressure include congestive heart failure & kidney disease. High blood pressure can have a huge impact on a person’s life. Overall, the incidence of hypertension is about the same in men and women. However, there are gender differences between age groups. In people under the age of 45, the incidence is higher in men; in the over 65 year age category, it is higher in women. There are also race differences; it is more common among African Americans than Caucasians and less likely to occur in Mexican-Americans. In the US, approximately 1 in 3 adults has high blood pressure, however most people are not aware they have this condition due to a lack of signs or symptoms.
High Blood Pressure Education Month encourages people to look at various lifestyle factors which may be contributing to high blood pressure. It is well documented that high levels of sodium (salt) is linked to high blood pressure. In the US, the majority of people consume more than twice the level of recommended sodium intake. Guidelines recommend up to 2,300mg of sodium per day for an adult. Those at higher risk should consume even less (up to 1,500mg of sodium a day). Higher risk groups include those who have diabetes, kidney disease, existing high blood pressure, and African American people.
Lifestyle changes which can help reduce blood pressure, include maintaining a healthy body weight, regular exercise, quitting smoking and following a healthy low sodium diet.
American Heart Month
The perfect gift this Valentine’s Day is the gift of heart health. Along with Valentine’s Day, February marks American Heart Month, a great time to commit to a healthy lifestyle and make small changes that can lead to a lifetime of heart health.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States. Every year, 1 in 4 deaths are caused by heart disease. The good news? Heart disease can often be prevented when people make healthy choices and manage their health conditions. Communities, health professionals, and families can work together to create opportunities for people to make healthier choices.
The American Heart Association recommends obese patients participate in a medically supervised weight loss program to reduce the risk of heart disease.